03/04/2025
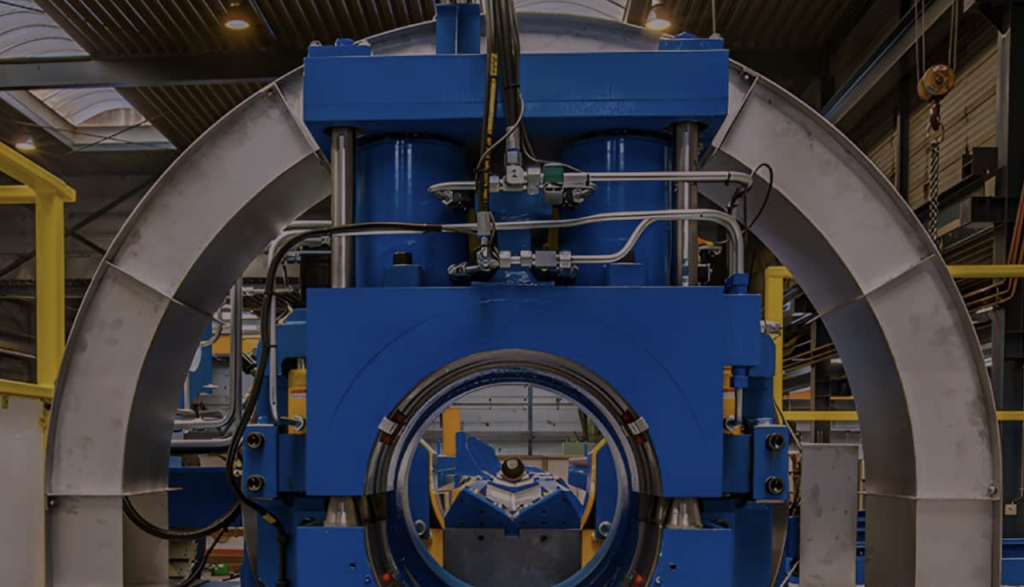
What is Induction Bending, High-Frequency Bending Machine?
 Induction Bending – Technical Explanation:
Induction Bending – Technical Explanation:
Induction bending is a precise and efficient method for bending pipes, tubes, or profiles using localized heating by electromagnetic induction.
 How It Works:
How It Works:
- Induction Coil Placement:
A high-frequency induction coil is placed around the section of the pipe where the bend is required. - Localized Heating:
The coil generates an alternating magnetic field that induces eddy currents in the metal, causing it to heat up rapidly—usually to 850–1100°C (depending on material type). - Bending Arm Mechanism:
Once the material is heated to plastic deformation temperature, a mechanical arm pushes the pipe through a fixed radius die to create a smooth bend. - Cooling (Quenching):
After bending, forced air or water spray is applied to cool and set the bend, preventing distortion or spring-back.
 Technical Advantages:
Technical Advantages:
- No thinning or wrinkling of pipe wall (maintains wall thickness).
- Accurate bend radius, from 5D to 100D or more.
- Large diameter pipes (up to 1,200 mm or more) can be bent.
- No need for internal mandrels or external dies.
- Suitable for carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, and titanium.
 High-Frequency Bending Machine:
High-Frequency Bending Machine:
A High-Frequency (HF) Bending Machine is a type of induction bending system that uses high-frequency (typically 3–100 kHz) alternating current to heat the material.
 Technical Features:
Technical Features:
- High-Frequency Generator: Produces the electromagnetic field.
- Precise Temperature Control: Allows controlled, repeatable heating cycles.
- CNC/PLC Systems: Automates the bend angle, heating duration, feed rate, and quenching.
 Where It’s Used:
Where It’s Used:
- Pipeline construction (oil, gas, water).
- Shipbuilding & offshore structures.
- Power plants (nuclear and thermal).
- Structural and architectural fabrication.
- Automotive & aerospace (for custom exhaust or structural components).
 Summary:
Summary:
| Feature | Induction Bending | High-Frequency Bending Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Heating method | Electromagnetic induction | High-frequency AC induction |
| Material types | Carbon steel, alloy steel, etc. | Same (with precision control) |
| Bend precision | High | Very high (CNC controlled) |
| Wall deformation | Minimal | Extremely minimal |
| Typical applications | Industrial piping, structures | High-precision industries |