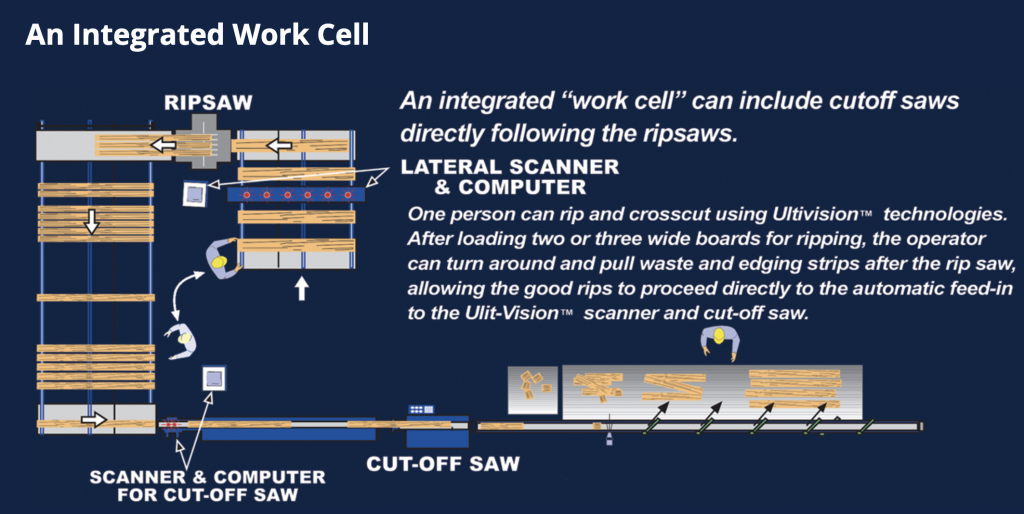
What is Lateral Wideboard Scanner for Rip Saws?
A Lateral Wideboard Scanner for Rip Saws is a specialized piece of equipment used in the woodworking industry, specifically in sawmills and lumber processing facilities. Its primary function is to optimize the cutting of wide boards or slabs of wood by providing detailed scanning and analysis before the material is fed into a rip saw. This scanner is crucial for maximizing yield, ensuring quality, and reducing waste during the ripping process.
Technical Explanation
- Purpose and Functionality:
- The Lateral Wideboard Scanner is designed to scan the entire surface of wide boards or slabs as they move laterally (sideways) on a conveyor system toward a rip saw. The scanner collects data on the board’s dimensions, defects, grain patterns, and other characteristics.
- This information is then used to determine the optimal cutting pattern for the rip saw, which splits the wide board into narrower pieces, such as planks or strips, according to desired dimensions and quality standards.
- Scanning Technology:
- Laser Scanners: The most common technology used in lateral wideboard scanners is laser scanning. Laser beams are projected onto the surface of the wood, and the reflected light is captured by sensors to create a detailed 3D profile of the board. This profile includes measurements of the board’s width, thickness, and flatness.
- Camera-Based Systems: Some scanners use high-resolution cameras in conjunction with laser scanners to capture both the 3D shape and surface features of the board. This allows for the detection of surface defects such as knots, cracks, and discoloration.
- X-Ray Scanners: In more advanced systems, X-ray technology may be used to see inside the wood, detecting internal defects like voids, rot, or hidden knots that are not visible on the surface. This helps in making more informed decisions about where to cut.
- Data Analysis and Optimization:
- The data collected by the scanner is processed by advanced software that analyzes the board’s characteristics. The software uses algorithms to determine the best way to cut the board to maximize yield while minimizing waste and defects.
- Optimization Parameters: The software can be programmed with various optimization parameters, such as desired board widths, quality grades, and defect tolerances. This allows the system to tailor the cutting plan to the specific needs of the mill or customer.
- Integration with Rip Saws:
- After scanning and analysis, the cutting plan is sent to the rip saw, which adjusts its cutting blades or saw positioning based on the optimized plan. Some systems are fully integrated, where the scanner and rip saw work in tandem, automatically adjusting in real-time as boards are fed through.
- Automatic Adjustments: In some setups, the rip saw can adjust its blades on-the-fly as the board passes through, based on real-time feedback from the scanner. This ensures that each board is cut with the highest efficiency and quality.
- Advantages:
- Maximized Yield: By accurately assessing the quality and dimensions of each board, the scanner helps mills extract the maximum usable material from each piece of wood, reducing waste and increasing profitability.
- Quality Control: The scanner ensures that only high-quality material is passed on for further processing, helping to maintain consistent product standards.
- Reduced Labor: Automation reduces the need for manual inspection and decision-making, allowing for faster processing and less reliance on skilled labor for optimization tasks.
- Flexibility: The system can handle a variety of wood types and sizes, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in lumber production.
- Challenges:
- Initial Cost: These systems can be expensive to install, particularly if they involve advanced technologies like X-ray scanning.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance and calibration are required to ensure the accuracy of the scanning and cutting processes.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating the scanner with existing machinery and workflows can be complex and may require significant adjustments to existing processes.
Summary
A Lateral Wideboard Scanner for Rip Saws is an advanced scanning system designed to optimize the cutting of wide boards in sawmills. It uses technologies such as laser scanning, camera-based systems, and sometimes X-rays to analyze the wood’s dimensions and defects. The data is then processed to create an optimal cutting plan, which is executed by the rip saw. This system maximizes yield, improves quality, and reduces waste, making it an essential tool in modern lumber processing.